2. Ray Tracer
The ray-tracer folder contains a serial ray tracer code (in a Fortran90 and a
C version), which computes a pretty picture. It writes the picture to a
file called result.pnm.
You can view the image under
- Linux with the display program (from the imagemagick package)
- Windows with irfanview.
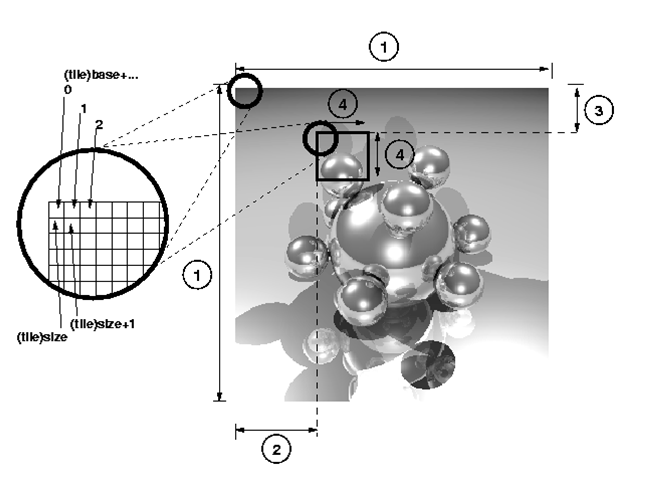
The central function is calc_tile, which computes one tile of the picture. The size of one tile and of the whole picture is hardcoded at the start of the main program.
NOTE: The code assumes that the picture size is a multiple of the tile size.
For this exercise, set them to 6000x6000 and 1000x1000, respectively, to begin with. The program outputs its runtime and its performance in million pixels per second (MPixel/s).
Compile
Compile the C or Fortran90 version of the ray tracer.
In order to compile an OpenMP program, you have to use
-fopenmpfor gcc, clang, gfortran, flang-new-qopenmpfor icc, ifort, icx, ifx
NOTE: the C version requires linking with -lm, that is the math library providing the sqrt and pow functions. Do this for example by: gcc -fopenmp ray-tracer.c -o ray-tracer -lm
Tasks
- Parallelize the code with OpenMP-parallel loops. You can deactivate the output for
testing, but make sure that your parallel code computes the correct
result (this is easy since you can always display the picture).
What speedup does your program get from 1 to N cores? - Do
you see any optimization potential in the way the code is parallelized?
Think about how the work is distributed among the threads, and how you
can influence this distribution.
- Tasking: Parallelize the code with OpenMP tasks. Is there a performance difference to the loop-parallel version? You might leave out counting the no. of tiles as task reductions are only partially working.
You can use `ray-tracer.task.c` or `ray-tracer.task.F90`. They include a check against a reference solution and print out the difference. This eliminates the need to view the image - Offloading: Offload the ray tracing to the GPU. We use the nvhpc compilers.
Load the compiler + cuda (on Alex cluster):
module purge
module load nvhpc cuda/12.3.0Compile your code with:
# C
nvc -O3 -march=native -Wall -Wextra -gopt -mp=gpu -gpu=cc80 ray-tracer.offload.c -o ray-tracer.offload.c.exe
# Fortran
You can use `ray-tracer-2.c` or `ray-tracer-2.F90`. They include a check
nvfortran -O3 -march=native -Wall -Wextra -gopt -mp=gpu -gpu=cc80 ray-tracer.offload.F90 -o ray-tracer.offload.F90.exeagainst a reference solution and print out the difference. This eliminates the need to view the image. Furthermore they do not include recursive calls inside the shade function.